The landscape of work is evolving, and we're at the cusp of a revolutionary shift. The modern workforce is becoming increasingly non-human. Enterprises are adopting agentic AI—AI agents designed to autonomously perform specific, purpose-driven tasks. These agents are not simply executing mundane operations; they are pushing the boundaries of task automation, creating an urgent need for rethinking how we secure their underlying mechanisms.
TL;DR
- Agentic AI will proliferate in the enterprise at a never-before-seen adoption rate to increase efficiency.
- Agentic AI is using and relying on Non-Human Identities (NHIs) to do its work.
- This situation makes the need to secure NHIs a pressing issue that must be addressed.
Automation has long been a driving force behind increased efficiency and innovation in enterprises. From streamlining repetitive tasks to enabling complex decision-making processes, automation technologies have transformed the way organizations operate. This evolution can be traced through three distinct stages: Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Hyperautomation, and now Agentic AI. Each stage represents a significant leap in capabilities and impact. However, as we embrace these advancements, a new challenge emerges—the rapid proliferation of NHIs. This surge introduces growing risks that, if left unmanaged, could reach a tipping point with serious implications for enterprise security.
A Diverse Landscape of Solutions
The rise of agentic AI has brought a diverse array of both open-source and commercial solutions to the table, offering flexibility and adaptability for enterprises. On one hand, open-source platforms provide customizable and cost-effective options; on the other hand, commercial solutions offer robust, enterprise-grade capabilities. This variety enhances innovation but also increases the complexity of ensuring comprehensive security across different technologies.
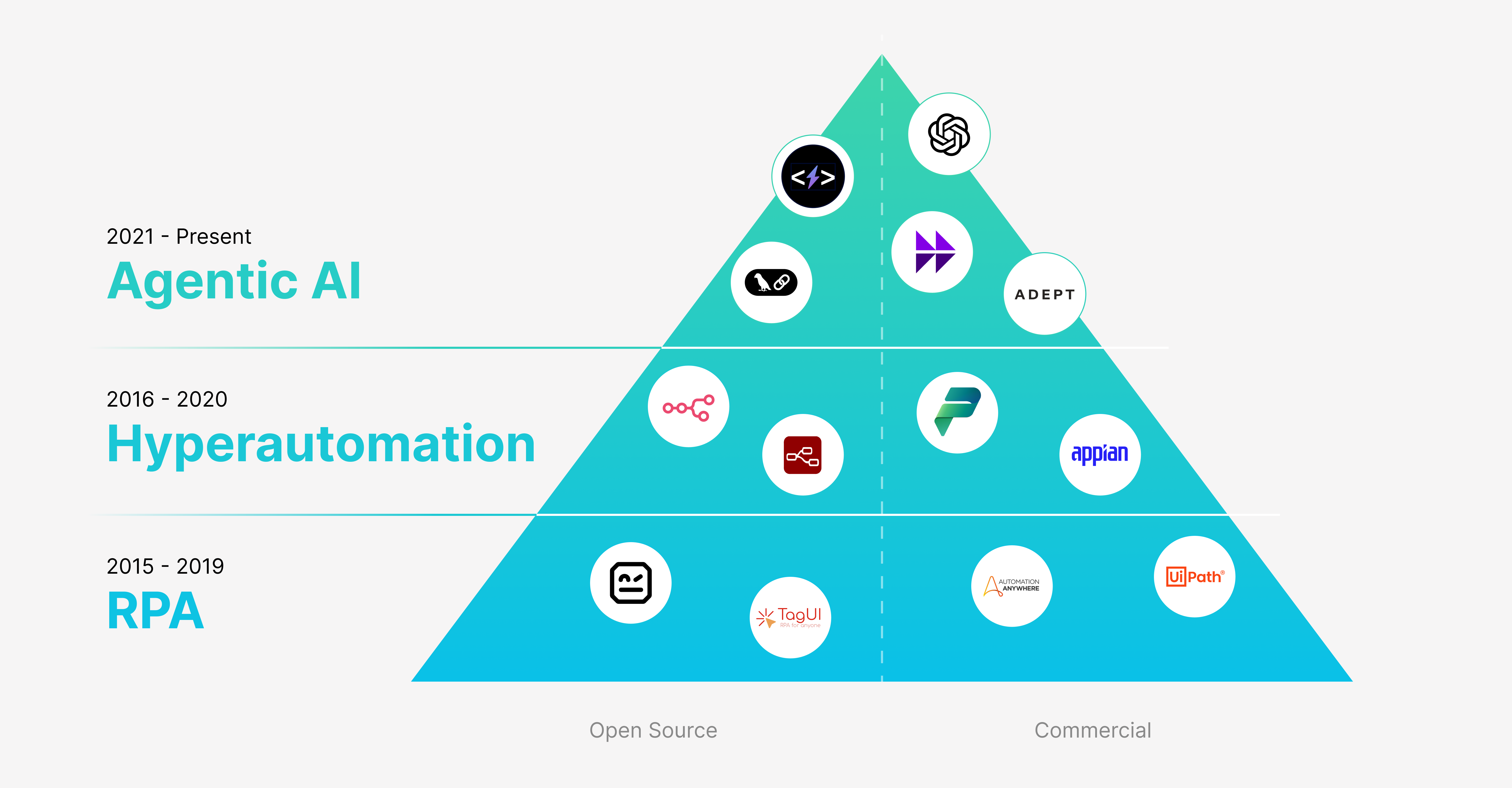
Stage 1: Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
The first step in the automation journey is Robotic Process Automation (RPA). This stage focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks using software robots. RPA tools are highly efficient for tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, or system integration—workflows that involve predictable sequences of actions.
Commercial solutions like UiPath and Automation Anywhere are leading examples that help organizations streamline routine business operations, reducing manual workload and increasing accuracy. On the open-source side, platforms like Robot Framework and TagUI have emerged as popular options, providing flexibility and adaptability for those seeking customizable automation without commercial licenses.
Stage 2: Hyperautomation
Building upon the foundations of RPA, the next stage in automation's evolution is Hyperautomation. It incorporates AI, machine learning, and decision-making capabilities to automate more complex processes. Hyperautomation aims to automate not just individual tasks but entire workflows, integrating data and decision-making across multiple systems.
In the commercial realm, platforms like Appian and Microsoft Power Platform (including Power Automate) offer sophisticated low-code environments that allow enterprises to combine RPA with AI to create intelligent workflows. Open-source alternatives like n8n.io and Node-RED provide extendable workflow automation tools that enable seamless integration of various services, making them accessible for a broader range of use cases.
Hyperautomation represents a significant step forward, expanding the scope of automation to encompass more nuanced and decision-based tasks, ultimately increasing operational efficiency and agility.
Stage 3: Agentic AI
As enterprises continue to seek greater autonomy and efficiency, Agentic AI emerges as the pinnacle of automation evolution. Agentic AI systems are capable of autonomous decision-making and task execution. They don’t just follow predetermined workflows—they learn, adapt, and act independently based on a defined purpose or set of objectives.
Commercial solutions like Moveworks, Adept AI, and OpenAI's GPT-4 provide sophisticated capabilities for autonomous task management and problem-solving. In the open-source space, platforms like LangChain and SuperAGI are enabling developers to create and deploy autonomous agents, pushing the boundaries of what non-human entities can achieve.
Agentic AI is poised to redefine the workforce by introducing self-directed agents capable of executing complex tasks without human intervention, creating both opportunities for growth and new challenges in identity security.
So What? The Urgent Need to Secure NHIs
With the rise of agentic AI comes an explosion in the use of Non-Human Identities (NHIs). This isn't a problem of a few years from now; it's happening right now, intensifying the already urgent issues of securing NHIs. Enterprises have long struggled with managing their legacy service accounts in Active Directory—a challenge as old as time. Now, they face the rapid adoption of agentic AI, which elevates the NHI challenge to a whole new level.
These AI agents need to authenticate to the systems they interact with, and they will not only use NHIs but also store and propagate them. We’re facing an unprecedented surge in the number of NHIs across enterprises, which brings with it a severe governance challenge. Who is keeping track of what these agents have access to? How can we ensure that these identities are not compromised?
Traditional methods of managing secrets and rotating credentials are no longer adequate. We’re moving into a future where the attack surface expands faster than the security controls we have in place. The urgency to adopt sophisticated NHI security solutions is clear: enterprises must get ahead of the risks that come with AI agents working autonomously or risk leaving the back door wide open.
The Workforce of Tomorrow: A Submerged Reality
Imagine the famous iceberg metaphor—where what is above the surface represents the visible, familiar human workforce, and the vast expanse below represents AI agents, largely unseen but forming the true bulk of the workforce. Just as global warming causes the sun (symbolizing rapid AI adoption and technological progress) to melt the tip of the iceberg (the human workforce), it floods the enterprise with agentic AI—expanding the submerged network of AI-driven tasks beneath.

This transformation is happening now, not in the distant future. The melting iceberg symbolizes how swiftly advancing technology is reshaping the workforce landscape. The human workforce is diminishing in proportion, while the non-human, AI-driven workforce grows exponentially beneath the surface. This is the modern workforce: largely non-human, complex, and increasingly autonomous. The pressing need to secure NHIs has never been more immediate.
The evolution we’re witnessing is not just about efficiency gains. It’s a tectonic shift in how work gets done, who (or what) performs it, and how secure we need to be in the methods and identities they use. To navigate this shift, organizations must recognize that the real workforce is the one operating below the surface—the agents, the NHIs, the non-human infrastructure holding everything together.
Urgency in Adopting NHI Security
The takeaway is simple but profound: enterprises must evolve their security practices as rapidly as they are adopting new AI technologies. The growth in AI agents directly correlates with an increase in NHIs, and without urgent action, the unmanaged proliferation of these identities will lead to significant security vulnerabilities. We need forward-looking solutions—ones that can keep pace with the agentic AI era.
To prepare for the future of work—a future driven by AI agents—enterprises must address the security challenges inherent in non-human identities. The time to act is now.